延迟
您是否需要执行以下任何操作?
- 在将来的某个时间安排活动
- 定期查询服务器或更新界面
- 将要执行的工作排队,这些工作必须等待其他初始化完成
- 执行大量计算
GWT 提供三个类,您可以使用它们将运行代码延迟到以后的某个时间点:Timer、DeferredCommand 和 IncrementalCommand。
安排工作:Timer 类
使用 Timer 类来安排将来要完成的工作。
要创建计时器,请创建一个 Timer 类的实例,然后覆盖 run() 方法入口点。
Timer timer = new Timer() {
public void run() {
Window.alert ("Timer expired!");
}
};
// Execute the timer to expire 2 seconds in the future
timer.schedule(2000);
请注意,计时器将不会有机会在控制权返回到 JavaScript 事件循环之前执行 run() 方法。
创建超时逻辑
计时器的一种典型用法是为长时间运行的命令设置超时。在这种情况下,有一些经验法则需要记住
- 将计时器存储在实例变量中。
- 在启动新计时器之前,始终检查计时器当前是否正在运行。(检查实例变量是否为 null。)
- 记住在命令成功完成时取消计时器。
- 在命令完成或计时器过期时,始终将实例变量设置为 null。
以下是如何使用 远程过程调用 (RPC) 的超时示例。
import com.google.gwt.user.client.Timer;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.Window;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.AsyncCallback;
public class Foo {
// A keeper of the timer instance in case we need to cancel it
private Timer timeoutTimer = null;
// An indicator when the computation should quit
private boolean abortFlag = false;
static final int TIMEOUT = 30; // 30 second timeout
void startWork () {
// ...
// Check to make sure the timer isn't already running.
if (timeoutTimer != null) {
Window.alert("Command is already running!");
return;
}
// Create a timer to abort if the RPC takes too long
timeoutTimer = new Timer() {
public void run() {
Window.alert("Timeout expired.");
timeoutTimer = null;
abortFlag = true;
}
};
// (re)Initialize the abort flag and start the timer.
abortFlag = false;
timeoutTimer.schedule(TIMEOUT * 1000); // timeout is in milliseconds
// Kick off an RPC
myService.myRpcMethod(arg, new AsyncCallback() {
public void onFailure(Throwable caught) {
Window.alert("RPC Failed:" + caught);
cancelTimer();
}
public void onSuccess(Object result) {
cancelTimer();
if (abortFlag) {
// Timeout already occurred. discard result
return;
}
Window.alert ("RPC returned: "+ (String)result);
}
}
}
// Stop the timeout timer if it is running
private void cancelTimer() {
if (timeoutTimer != null) {
timeoutTimer.cancel();
timeoutTimer = null;
}
}
}
定期运行逻辑
为了保持用户界面的最新,有时您希望定期执行更新。您可能希望运行对服务器的轮询以检查是否有新数据,或者更新屏幕上某种动画。在这种情况下,使用 Timer 类 scheduleRepeating() 方法
public class Foo {
// A timer to update the elapsed time count
private Timer elapsedTimer;
private Label elapsedLabel = new Label();
private long startTime;
public Foo () {
// ... Add elapsedLabel to a Panel ...
// Create a new timer
elapsedTimer = new Timer () {
public void run() {
showElapsed();
}
};
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Schedule the timer for every 1/2 second (500 milliseconds)
elapsedTimer.scheduleRepeating(500);
// ... The elapsed timer has started ...
}
/**
* Show the current elapsed time in the elapsedLabel widget.
*/
private void showElapsed () {
double elapsedTime = (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) / 1000.0;
NumberFormat n = NumberFormat.getFormat("#,##0.000");
elapsedLabel.setText("Elapsed: " + n.format(elapsedTime));
}
}
将某些逻辑推迟到不久的将来:Scheduler 类
有时您希望中断逻辑循环,以便 JavaScript 事件循环有机会在两段代码之间运行。 Scheduler 类将允许您这样做。传递给 Scheduler 的逻辑将在将来某个时间点运行,在控制权返回到 JavaScript 事件循环之后。这个小小的延迟可能会让界面有机会处理一些用户事件或初始化其他代码。要在最简单的形式中使用 Scheduler 类,请创建一个 Command 类的子类,覆盖 execute() 方法并将其传递给 Scheduler.scheduleDeferred
TextBox dataEntry;
// Set the focus on the widget after setup completes.
Scheduler.get().scheduleDeferred(new Command() {
public void execute () {
dataEntry.setFocus();
}
});
dataEntry = new TextBox();
避免缓慢脚本警告:IncrementalCommand 类
AJAX 开发人员需要意识到让浏览器对用户保持响应。当 JavaScript 代码正在运行时,按钮和文本区域等用户界面组件将不会响应用户输入。如果浏览器允许这种情况继续,用户可能会认为浏览器“挂起”并试图重新启动它。但浏览器有一个内置的防御机制,即*无响应脚本警告*。
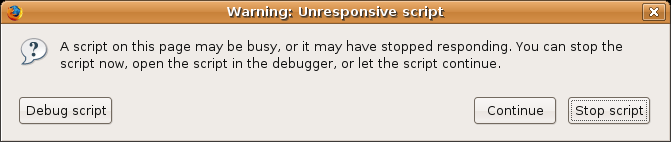
任何在不将控制权返回到 JavaScript 主事件循环的情况下运行超过 10 秒或更长时间的脚本都可能导致浏览器向用户弹出一个对话框。该对话框的出现是因为编写不当的脚本可能存在无限循环或其他导致浏览器无法响应的错误。但在 AJAX 应用程序中,脚本可能正在执行合法的工作。
GWT 提供一个 IncrementalCommand 类,它有助于执行长时间运行的计算。它通过重复调用‘execute()’入口点来工作,直到计算完成。
以下示例概述了如何使用 IncrementalCommand 类以一种允许浏览器用户界面保持响应的方式进行一些计算
public class IncrementalCommandTest implements EntryPoint {
// Number of times doWork() is called
static final int MAX_LOOPS = 10000;
// Tight inner loop in doWork()
static final int WORK_LOOP_COUNT = 50;
// Number of times doWork() is called in IncrementalCommand before
// returning control to the event loop
static final int WORK_CHUNK = 100;
// A button to kick off the computation
Button button;
public void onModuleLoad() {
button = new Button("Start Computation");
button.addClickHandler(new ClickHandler () {
public void onClick(ClickEvent event) {
doWorkIncremental();
}
}
}
/**
* Create a IncrementalCommand instance that gets called back every so often
* until all the work it has to do is complete.
*/
private void doWorkIncremental () {
// Turn off the button so it won't start processing again.
button.setEnabled(false);
IncrementalCommand ic = new IncrementalCommand(){
int counter = 0;
public boolean execute() {
for (int i=0;i<WORK_CHUNK;i++) {
counter++;
result += doWork();
// If we have done all the work, exit with a 'false'
// return value to terminate further execution.
if (counter == MAX_LOOPS) {
// Re-enable button
button.setEnabled(true);
// ... other end of computation processing ...
return false;
}
}
// Call the execute function again.
return true;
}
};
// Schedule the IncrementalCommand instance to run when
// control returns to the event loop by returning 'true'
Scheduler.get().scheduleIncremental(ic);
}
/**
* Routine that keeps the CPU busy for a while.
* @return an integer result of the calculation
*/
private int doWork() {
int result;
// ... computation...
return result;
}